The Ultimate Guide to Agency Management Software
Think of agency management software as the central nervous system for your entire operation. It's the one place where everything connects, designed to bring sanity and clarity to the often-chaotic world of agency life. It’s not just another app to add to your tech stack; it's a unified system that pulls project management, client relationships, team scheduling, and financials under one roof.
What Is Agency Management Software
Picture trying to conduct a symphony orchestra where every musician is playing from a different sheet of music. The result would be a mess, right? That’s what happens when agencies try to run on a mix of disconnected spreadsheets, scattered email threads, and a handful of single-purpose project tools. Details get lost, deadlines slip, and figuring out if you're actually profitable feels more like guesswork than a business calculation.
This is the exact operational friction that agency management software is built to eliminate. It steps in as the conductor, making sure every part of your agency—from that first client pitch to the final invoice—is playing in perfect harmony.
Moving Beyond Disconnected Tools
So many agencies start out by duct-taping various apps together. You might have one tool for your to-do lists, another for tracking hours, and a separate CRM to keep client info straight. While that might work when you're small, it quickly leads to information silos and a whole lot of administrative drag as you grow.
A true agency management system replaces that patchwork with a single source of truth. Instead of your team wasting time copy-pasting information from one system to another, everything just flows. This solves a few huge, all-too-common headaches:
- No Real Visibility: You get a clear, real-time picture of project progress, who’s overworked (and who’s not), and the financial health of the business.
- Wasted Admin Time: By automating things like pulling reports, generating invoices, and sending reminders, it frees up your team to do what they do best: creative, billable work.
- Inaccurate Project Costing: When time tracking is directly linked to projects and billing, you can finally see which clients and which types of projects are actually making you money.
There's a reason the market for these platforms is booming. Valued at USD 4.30 billion in 2024, the global Agency Management Software market is expected to hit USD 6.53 billion by 2030. This isn't just hype; it reflects a serious need for tools that can cut operational costs—often by up to 30% through automation, according to a business research report—while client demands just keep getting higher.
Think of it this way: Your agency's talent is its engine, but agency management software is the chassis, transmission, and steering wheel. It provides the structure that allows your team's creative power to move in the right direction, efficiently and at scale.
At the end of the day, this software is the operational backbone you need to grow sustainably. It transforms scattered efforts into a focused, profitable, and scalable business.
Understanding The Core Features
Agency management software isn't just one giant tool. Think of it more like a central nervous system for your business, made up of interconnected modules that talk to each other. Each part handles a specific function, but when they work together, they get rid of the data silos and administrative headaches that kill momentum.
It’s a bit like a modern car. You have an engine, a transmission, and an electrical system. Each has its own job, but it's how they all integrate and communicate that gives you a smooth, efficient, and reliable ride.
Let's pop the hood and look at the essential components that make these systems work, going beyond a simple feature list to get at the why behind each module.
To better understand how these pieces fit together, here’s a quick overview of what each module does, the problem it solves, and the direct benefit it brings to your agency.
Core Modules of Agency Management Software at a Glance
| Core Module | Primary Function | Problem It Solves | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Project Management | Task creation, assignment, and progress tracking | Disorganized workflows, missed deadlines, and chaotic communication. | A single source of truth for all project-related activities, ensuring clarity and on-time delivery. |
| Client Relationship Management (CRM) | Storing all client interactions, history, and contact data. | Lost context, inconsistent client communication, and missed opportunities. | A unified client view that enables proactive service and stronger, long-term relationships. |
| Resource Scheduling | Visualizing and allocating team member workloads and availability. | Team burnout from over-allocation and lost revenue from under-utilization. | Optimized team capacity, leading to improved project profitability and employee satisfaction. |
| Financial Management | Invoicing, expense tracking, time tracking, and profitability analysis. | Inaccurate project estimates, profit leaks, and delayed financial insights. | Real-time visibility into project and client profitability, enabling smarter business decisions. |
Now, let's dig a little deeper into the role each of these core components plays in the day-to-day life of a busy agency.
The Engine Room: Project Management
At its core, an agency's product is organized execution. The project management module is the engine that drives this entire process, turning great ideas into real deliverables on a predictable timeline. This is where tasks get created, handed off, and tracked from the first kickoff meeting to the final sign-off.
This module gives everyone a single, shared view of all active projects, showing you exactly where everything stands at a glance. It instantly answers the questions that bog down your team: What’s due this week? Who’s handling the next step? Are we going to hit our deadline?
Without it, teams are stuck juggling scattered to-do lists and endless status update meetings. In fact, some studies show employees can waste over 5 hours a week just hunting for information or chasing down colleagues for updates. This module puts an end to that by bringing all that activity into one place.
The Communications Hub: Client Relationship Management
Your client relationships are your agency's most valuable asset. The Client Relationship Management (CRM) module acts as the central hub for every conversation, decision, and piece of data related to each client. It's essentially your agency's collective memory.
This is where you store everything from the first email and contract details to meeting notes and ongoing correspondence. Imagine your account manager hopping on a call, able to instantly pull up every past interaction. They're not just better prepared; they can deliver a much higher level of service.
A good CRM built directly into your agency management software ensures that nothing falls through the cracks. If a key team member is out sick, someone else can step in with the full context of the relationship at their fingertips. This prevents frustrating communication gaps and makes clients feel genuinely understood.
The Air Traffic Controller: Resource Scheduling
One of the biggest juggling acts for any agency is managing team capacity. The resource scheduling module is your air traffic controller, giving you a crystal-clear view of who is working on what, when they're free, and whether their workload is balanced.
Its main job is to prevent the two extremes: over-allocation, which leads straight to burnout, and under-allocation, which quietly eats away at your profitability. By visualizing team schedules, managers can assign tasks based on actual availability, not just a gut feeling. This is absolutely critical for planning future projects and giving new clients realistic timelines.
Let's say a hot new project lands in your lap. With resource scheduling, you can immediately see that your lead designer is slammed for the next two weeks. This lets you make a proactive choice—either adjust the project timeline or line up a freelancer—instead of reacting to a fire you didn't see coming.
Getting this right is huge. Agencies that master resource management can often improve their billable utilization rates by 10-15%, which is a direct boost to the bottom line.
The Profitability Dashboard: Financial Management
Finally, the financial management module is what connects all the day-to-day work to your agency's financial health. It’s the profitability dashboard that tells you if all that creative effort is actually paying off. This is where you manage invoicing, track expenses, and, most importantly, run your job costing.
By pulling time tracking data from the project management module and tying it to employee rates, the system gives you real-time profitability reports for every single project and client. You no longer have to wait for the quarterly P&L to find out that a fixed-fee project went completely off the rails.
This direct line of sight into your financials helps you make much smarter business decisions. You can pinpoint which types of projects are your cash cows, which clients are draining resources, and where you need to tweak your pricing or process to plug profit leaks. It transforms financial oversight from a reactive chore into a powerful strategic advantage.
What Are the Real Business Benefits of an Integrated System?
Let's move past the feature lists for a moment. The real magic of agency management software isn't just about having cool tools; it's about the tangible results it brings to your business day in and day out. An integrated system doesn't just tidy things up—it makes your agency healthier, more profitable, and ready to scale. It’s the difference between constantly plugging leaks in a manual-process boat and sailing smoothly in a vessel built for growth.
The most immediate change you'll notice is a massive leap in operational efficiency. When project details, time tracking, and client messages all live under one roof, the administrative drag that bogs down your team simply vanishes. Think of all the hours you'll get back—no more hunting for that one email, fixing spreadsheet errors, or trying to stitch together reports from three different apps.
Immediately Boost Your Project Profitability
This is where you’ll feel the impact first: your bottom line. So many agencies fly blind when pricing fixed-fee projects, essentially guessing how much effort a job will actually take. With time tracking and project costing built right in, you finally get a crystal-clear view into the profitability of every single project.
This kind of visibility lets you stop profit leaks before they sink you. For example, you might discover you’re consistently underwater on website redesigns but killing it on your content retainers. Armed with that hard data, you can finally make informed decisions—adjust your pricing, tighten up your process for those less profitable services, or double down on selling what you know makes money.
Real-World Impact: We worked with an agency that felt they were spinning their wheels—busier than ever, but with profits staying flat. After getting their data into one system, they uncovered that unchecked scope creep was eating away 15% of their margin on fixed-fee work. With real-time insights, they were able to course-correct and hit a consistent 20% profit margin in just six months.
Elevate Client Satisfaction and Keep Them Coming Back
A unified system completely changes the game for your client relationships. When anyone on your team can pull up a complete history of every client interaction—from the first call to the latest feedback—they can deliver service that’s faster, smarter, and more personal. Things stop falling through the cracks, and your clients feel genuinely looked after.
This naturally leads to more transparency and trust. You can pull a status report, share a progress update, or send a clear invoice without a frantic scramble to gather information. That level of professionalism and organization builds serious client confidence, which is the bedrock of retention and referrals.
- One Source of Truth: Any team member can jump in on a client conversation with full context.
- Transparent Reporting: Build trust by easily sharing accurate progress and budget updates.
- Proactive Service: Get a complete view of the client relationship to spot potential issues or opportunities early.
Reclaim Your Team’s Time Through Smart Automation
Repetitive admin work is the silent killer of agency productivity and morale. A good agency management software automates these soul-crushing tasks, freeing up your talented people to focus on the creative, strategic work they were hired to do.
This isn’t just about one or two tasks; automation can be woven throughout your entire workflow:
- Automated Invoicing: Set up recurring invoices for retainers or have them generated automatically from tracked time and expenses. No more end-of-month scramble.
- Task Reminders: Let the system nudge people about deadlines, so your project managers don't have to.
- Report Generation: Schedule profitability, utilization, and project health reports to land in your inbox right when you need them.
The combined effect of all this is huge. There's a reason this software market is booming—it’s become the operational backbone for any agency that wants to compete. North America currently accounts for over 40% of the global market share as agencies race to optimize their workflows and cut down on waste. With cloud-based platforms expected to hit 60% market penetration by 2025, agencies using these systems are reporting efficiency gains as high as 50%. You can dig deeper into these trends in this comprehensive market analysis. The takeaway is clear: integrated software is no longer a "nice-to-have." It's a fundamental part of running a modern, scalable agency.
How to Choose the Right Software for Your Agency
Picking the right agency management software is one of the most critical decisions you'll make. This isn't just about buying another tool; it's about choosing an operational partner. Get it right, and it can feel like you just added a seasoned COO to your team overnight. Get it wrong, and you'll saddle your team with friction, clunky workflows, and constant frustration.
Making a smart choice means you have to look past the slick sales demos and really pressure-test whether a platform fits your agency's unique DNA. It comes down to a structured approach: getting brutally honest about your needs, running real-world trials, and asking the tough questions that reveal a platform's true colors. The goal is to find a system that helps you grow not just today, but for the next five years.
Start With a Deep Internal Needs Analysis
Before you even glance at a software website, you need to look in the mirror. The single biggest mistake agencies make is chasing shiny new features instead of solving the problems they actually have.
Get your team leads in a room—project management, accounts, finance, the works. Map out your biggest headaches. What are the top three things that grind your team to a halt every week? Where does communication always seem to break down? What simple financial question (like "Are we profitable on this project?") can you not answer right now?
This exercise should give you a crystal-clear list of "must-haves" versus "nice-to-haves."
- Must-Have: A seamless, two-way sync with QuickBooks to stop manual invoice entry.
- Must-Have: A resource planning view that helps us see who's overbooked before they burn out.
- Nice-to-Have: A client-facing portal for sharing files and updates.
This internal audit is your North Star. It keeps you focused on what truly matters and stops you from getting distracted by bells and whistles that won't actually improve your business.
Key Decision Criteria to Focus On
With your needs clearly defined, you can start sizing up the options. I always tell agencies to evaluate platforms against three core pillars: scalability, integrations, and user experience. Think of these as the absolute non-negotiables that will determine if the software adds value or just adds noise.
1. Scalability: Can It Grow With You?
The software that works for a five-person shop will completely fall apart for a 25-person agency. You need a platform that can handle more projects, more clients, and a bigger team without lagging, bugging out, or becoming a convoluted mess. Ask vendors directly how their system performs under pressure and what their roadmap looks for supporting larger teams.
2. Integrations: Does It Play Well With Others?
Your agency management software is the hub, but it's not the only spoke in the wheel. It absolutely has to connect with the other tools you depend on every day, whether that's Slack, Google Drive, or your accounting platform. Bad integrations mean someone on your team is stuck doing manual data entry, which completely defeats the purpose of a central system.
3. User Experience (UX): Will Your Team Actually Use It?
This is, without a doubt, the most important and most frequently ignored factor. It doesn’t matter how powerful a platform is if your team dreads logging in. A clean, intuitive interface is everything. If it takes a 30-minute training video to teach someone how to log their time, you're going to have an adoption nightmare. In fact, a recent study showed that nearly 70% of employees feel more productive when their software is easy to use.
The Litmus Test: During a demo or trial, can a brand-new team member figure out how to update a task or log their time in under five minutes, without a tutorial? If the answer is no, you have a serious UX problem on your hands.
Run Effective Trials and Demos
Never, ever commit to a platform based on a sales pitch alone. You have to get your hands dirty. Sign up for a free trial and assign a small, cross-functional "test crew" to run a real (or at least realistic) project through it. This is where the marketing promises meet reality.
To keep things objective, create a simple checklist to grade each contender. This helps you compare apples to apples and make a decision based on facts, not just a gut feeling.
Here's a practical checklist you can adapt to guide your team's evaluation process. It ensures you're asking the same critical questions for every platform you test.
Software Evaluation Checklist
| Evaluation Criteria | Question to Ask | Importance (High/Medium/Low) |
|---|---|---|
| Project Setup | How quickly can we spin up a new project with tasks, timelines, and a budget? | High |
| Time Tracking | Is it truly simple for team members to log time against specific tasks? | High |
| Reporting | Can I pull a real-time report on project profitability or team utilization? | High |
| Integrations | Does it connect seamlessly with our essential tools like QuickBooks and Slack? | High |
| Mobile Access | Is the mobile app actually functional for on-the-go updates, or is it an afterthought? | Medium |
| Support | If we have an urgent issue, what’s the real-world response time from support? | Medium |
By the end of this process, you’ll have a clear winner based on how each platform performed against the needs that matter most to your agency.
Following this structured evaluation takes the guesswork out of the equation. You're no longer just "buying software"; you're making a calculated, strategic investment in your agency's future efficiency and profitability.
A Roadmap for Successful Implementation
Switching your agency management software can feel like performing open-heart surgery on your business. Let's be honest—it’s a huge operational shift that touches every single person on your team. But with a clear roadmap, you can make the transition surprisingly smooth, keep downtime to a minimum, and get your team to actually love the new system instead of resent it.
Success here isn't just about the tech; it's about the people. This is fundamentally a change management project. Getting your team on board from the very beginning is the single biggest predictor of whether this investment will pay off. If you rush it, you're practically guaranteeing resistance and low adoption down the line.
Phase 1: Pre-Implementation Planning
Before you even think about moving a single byte of data, you need to lay the groundwork. This is all about preparation and getting everyone on the same page. Think of it as drawing up the architectural blueprints before the construction crew shows up. A little diligence here prevents massive headaches later.
First things first: clean your house. Run a thorough data audit. Get rid of those duplicate client contacts, archive ancient projects that are cluttering things up, and standardize how you format everything. Migrating messy data into a shiny new system is like moving piles of junk into a brand-new home—you’re just creating new problems in a nicer-looking place.
Next, map out your current workflows. How does a project really move from a sales call to a happy client right now? Documenting this stuff often reveals all sorts of hidden bottlenecks and gives you a clear picture of how to set up the new software for a much smarter future. This is also the perfect time to pull together your implementation team—a small group of champions from different departments who will help steer the ship.
This simple visualization shows the core steps in the software selection process that precedes implementation.
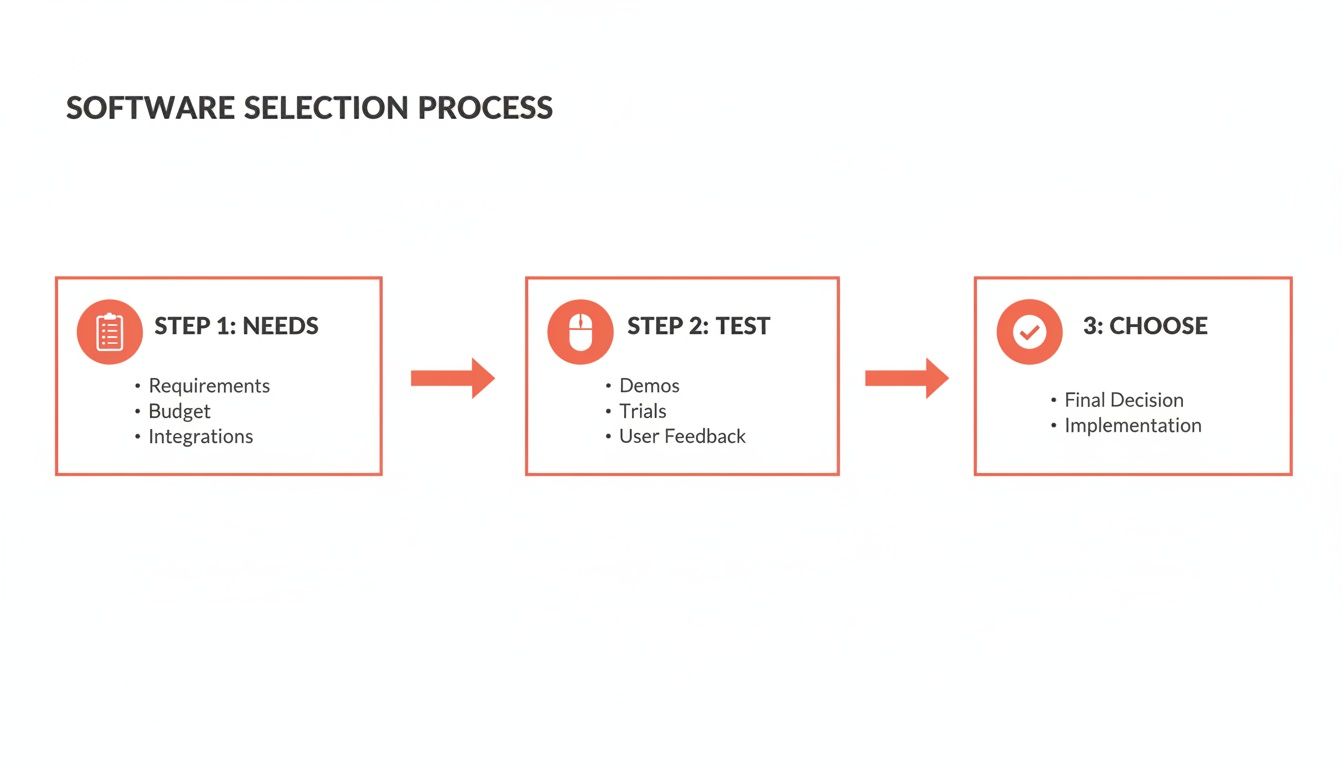
This process ensures that by the time you reach implementation, your choice is already aligned with your agency's core operational needs.
Phase 2: The Implementation and Go-Live
Okay, plan in hand, it's time for the technical part. This is where you'll set up the software, migrate your squeaky-clean data, and configure the platform to match those new-and-improved workflows you designed. Whatever you do, don't try to boil the ocean and do everything at once.
Pro Tip: Start with a pilot project. Pick one or two smaller, low-risk projects and run them from start to finish only in the new system. This lets a small team learn the ropes in a real-world setting, iron out any kinks, and become your internal experts who can help train everyone else.
This approach builds momentum. As your pilot team starts talking about how much easier things are, you'll build genuine excitement across the agency. Once the pilot is a success and you've made your tweaks, you can schedule the full "go-live" for the rest of the company. Make sure to celebrate this milestone—it’s a big deal!
Phase 3: Post-Launch Support and Training
The work isn't over when you flip the switch. In fact, this is where the real work begins: making the new system a core part of your team's daily habits. This is why effective, ongoing training is non-negotiable.
Don't just herd everyone into a single two-hour webinar and call it a day. People learn differently, so you need a mix of resources:
- Live Training Sessions: Walk through the key workflows for specific roles. Show your project managers, designers, and account managers exactly how the system makes their jobs easier.
- On-Demand Resources: Build a library of short video tutorials and one-page cheat sheets. Nobody wants to dig through a 50-page manual to find one answer.
- Office Hours: Set aside time each week where anyone can drop in with questions and get one-on-one help.
Finally, set up a feedback loop. The goal is continuous improvement, not just sticking to a plan you made three months ago. Encourage your team to suggest tweaks and better ways of doing things. As your agency evolves, your agency management software should evolve right along with it.
Calculating Your True Return on Investment
Let’s be honest: buying new software feels like an expense. But thinking of an agency management software as just another line item is a mistake. It’s a strategic investment, and like any good investment, it should deliver a clear return. To get buy-in, you need to build a business case that goes beyond the monthly subscription fee and calculates the real, tangible Return on Investment (ROI).
This isn't about fuzzy math or vague promises. It’s about pinning down the actual gains in efficiency, billable hours, and project margins. The core question is simple: how much value does this platform create versus how much does it cost? When you can answer that, you’ve proven the software is a growth engine, not just a cost center.
Quantifying Gains and Calculating ROI
So, where do you start? The most significant financial impacts usually come from three places: reclaimed time, better project profitability, and lower administrative overhead. Once you put a number on those gains, the rest is simple arithmetic.
The classic formula looks like this:
ROI Formula: (Financial Gain from Investment – Cost of Investment) / Cost of Investment
The tricky part is figuring out the "Financial Gain." Let's walk through a real-world example to make it concrete.
Imagine you have 10 project managers, and their billable rate is $100 an hour. You run a trial of a new platform and find it saves each PM just two hours a week—time they previously spent chasing down task updates and manually building reports. It doesn't sound like much, but watch how it adds up.
- Weekly Reclaimed Hours: 10 PMs x 2 hours/week = 20 hours
- Monthly Reclaimed Hours: 20 hours/week x 4 weeks = 80 hours
- Monthly Value Gained: 80 hours x $100/hour = $8,000
Now, let's say the software costs $1,500 per month. Your monthly ROI is:
($8,000 – $1,500) / $1,500 = 4.33 or a 433% return.
Suddenly, that $1,500 looks like a bargain. And this is a conservative estimate. We haven't even touched on catching scope creep before it gets out of hand, cutting down non-billable admin time for the entire team, or using utilization data to make smarter staffing decisions.
Beyond Time Savings: The Hidden Multipliers
Reclaimed billable hours are the easiest metric to calculate, but they’re just the beginning. The right platform has a multiplier effect, creating value that compounds across your entire operation. It’s the hidden ROI that often makes the biggest difference.
Think about these other financial wins:
- Improved Project Margins: When you have real-time data on job costs, you can see profit leaks as they happen, not a month later. Catching just one over-serviced project before it goes deep into the red can save you thousands.
- Reduced Overhead: How many hours does your finance lead spend chasing timesheets or manually piecing together invoices? Automating that grunt work frees them up for strategic financial planning.
- Increased Client Retention: Smoother projects and clearer communication create happy clients. Happy clients stick around, and that directly impacts their lifetime value.
When you build your business case, start with the hard numbers from the time-savings calculation. Then, layer in these powerful secondary benefits. It completely changes the conversation from, "Can we afford this?" to, "How can we afford not to do this?"
Frequently Asked Questions
It's a big decision, choosing a new operational backbone for your agency. So, naturally, you're going to have some questions. We've gathered some of the most common ones we hear from agency leaders and answered them directly, without the fluff.
How Long Does Implementation Typically Take?
There’s no magic number here—it really depends on the size of your agency and how much data you’re bringing over. For a smaller, more agile team, you could be fully operational in just a few weeks. But for a larger agency with a decade of project history to migrate, you're probably looking at a two-to-three-month journey.
A few key things will shape your timeline:
- Data Migration: How much client, project, and financial data do you have? And more importantly, how clean is it?
- Customization: Do you need to set up highly specific workflows, or will the out-of-the-box setup work for you?
- Team Training: How much time can you realistically dedicate to getting everyone comfortable and confident with the new system?
Pro tip: Try a phased rollout. Kicking things off with a single pilot project can make the whole process feel much smoother and helps build momentum.
Will This Software Integrate With My Accounting Tools?
It absolutely should. A good agency management platform is meant to be your central source of truth, not another data island you have to paddle to. Solid integrations aren't a nice-to-have; they're a must for running a tight ship.
Most of the top platforms are built to play nicely with the tools agencies already use every day, like QuickBooks and Xero. They often connect with communication apps like Slack and cloud storage like Google Drive too. But always, always double-check that your mission-critical integrations are supported before you sign anything.
What's The Biggest Mistake Agencies Make When Adopting New Software?
Without a doubt, the most common pitfall is fumbling the change management. You can buy the most powerful, feature-rich software on the market, but if your team doesn't actually use it in their day-to-day work, it’s a failure.
The real measure of success for any new software isn't its feature list—it's the adoption rate. If your team doesn't embrace it, the investment is wasted.
The key to avoiding this is putting your people first. Bring your team into the selection process early and ask for their input. When it's time to learn the system, provide thorough training that’s specific to their roles, showing them exactly how it makes their jobs easier.
Finally, find a few internal champions—people who are genuinely excited about the new platform. They can offer peer support and keep the energy high. This turns what could be a disruptive change into a genuine team upgrade.
Ready to stop duct-taping your operations together and install a true OS for your agency? RGK is the unified platform built to help you run, grow, and keep your business without the chaos.